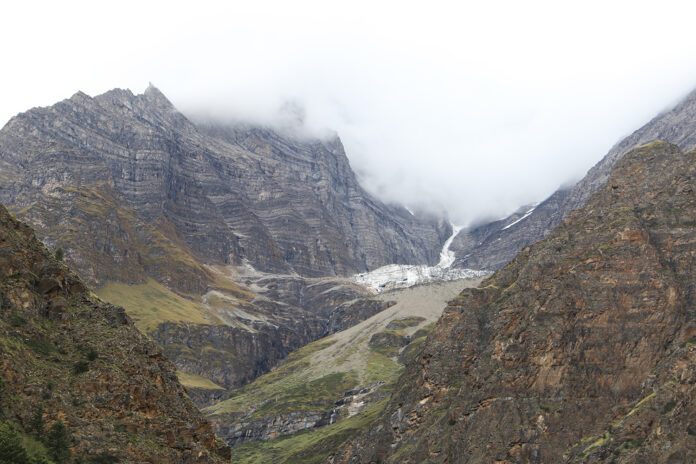
Kathmandu 9 Jan 2022 The Himalayan region of Nepal is experiencing significant impacts due to climate change, affecting its glaciers, ecosystems, and local communities. Simultaneously, journalism in Nepal faces numerous challenges, including threats to press freedom, economic constraints, and the evolving media landscape. This article examines the effects of climate change in Nepal’s Himalayas and explores the difficulties encountered by journalists between 2020 and 2022.
Nepal, home to a substantial portion of the Himalayan mountain range, is highly vulnerable to climate change. The region’s glaciers are retreating, leading to altered water resources and increased risks of natural disasters. Concurrently, the field of journalism in Nepal grapples with issues such as press freedom violations, economic hardships, and the rapid digital transformation of media. This article delves into the intersection of these two critical areas, focusing on developments from 2020 to 2022.
Climate Change in Nepal’s Himalayan Region
Glacial Retreat and Melting
The Himalayas, often referred to as the “Third Pole,” contain vast glacial reserves that are crucial for water supply in South Asia. However, these glaciers are retreating at an alarming rate due to rising temperatures. A study published in 2023 highlighted that Nepal’s glaciers have been shrinking significantly, with notable reductions in area and volume over recent decades.
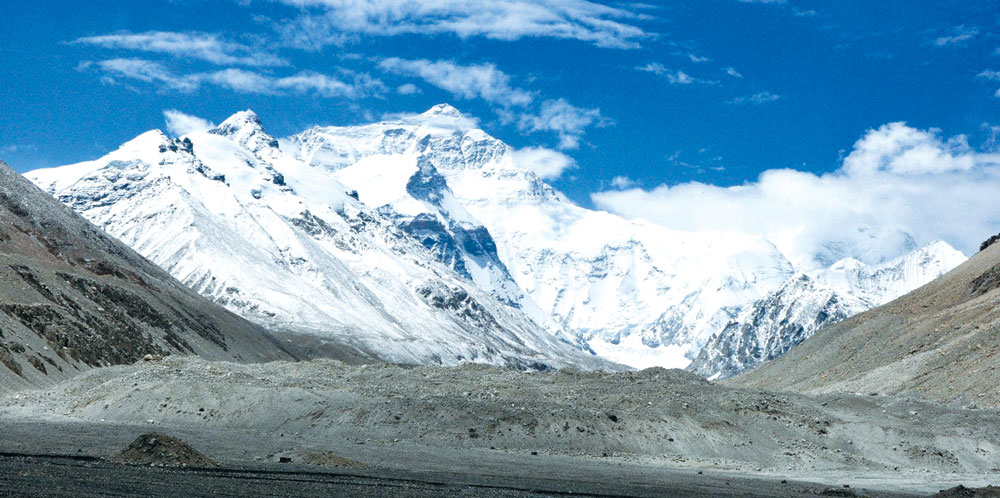

The melting of glaciers has led to the formation and expansion of glacial lakes, increasing the risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs). These events pose significant threats to downstream communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems. For instance, the Melamchi River experienced extreme flooding in June and July 2021, causing widespread damage and highlighting the urgent need for effective climate adaptation strategies.
Impact on Water Resources
Glacial meltwater is a vital component of Nepal’s river systems, supporting agriculture, hydropower, and domestic water needs. The accelerated melting of glaciers disrupts the seasonal flow of rivers, leading to water scarcity during dry periods and increased flooding during monsoons. This variability poses challenges for water resource management and affects the livelihoods of millions who depend on consistent water supply.
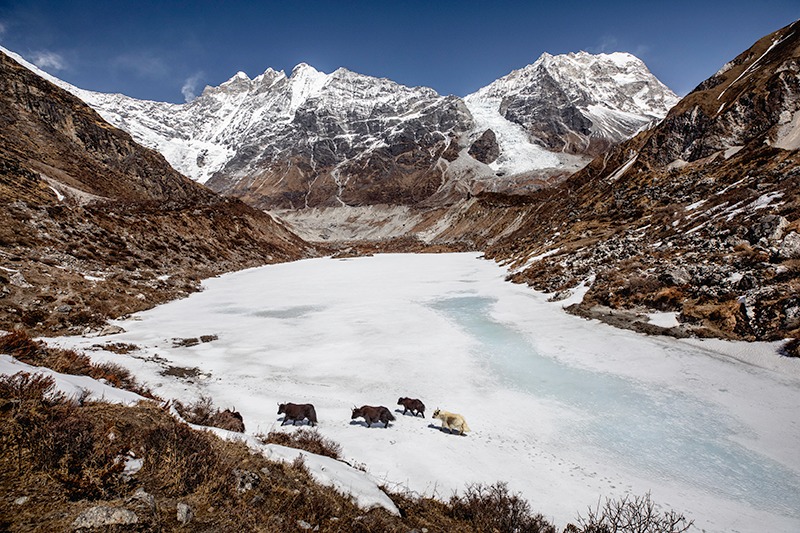

Biodiversity and Ecosystem Changes
Climate change has profound effects on the biodiversity of the Himalayan region. Shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns alter habitats, affecting flora and fauna. Species adapted to specific climatic conditions may face extinction if they cannot migrate to suitable environments. Additionally, the timing of biological events, such as flowering and breeding seasons, is changing, leading to mismatches in ecological interactions.
Socioeconomic Impacts
The communities residing in the Himalayan region are predominantly dependent on agriculture, tourism, and natural resources. Climate-induced changes threaten these livelihoods. For example, the traditional honey harvesting practices of the Gurung community are under threat due to a decline in bee populations, largely attributed to climate change. Harvesters have reported a drastic reduction in honey yield, impacting their income and cultural practices.
Challenges Faced by Journalism in Nepal (2020-2022)
Press Freedom and Safety
Journalists in Nepal have faced increasing threats to press freedom. The Federation of Nepali Journalists reported that 2022 was particularly challenging, with new methods being adopted to curb freedom of the press through digital means. Attacks on media organizations and journalists have added to the challenges in the field of Nepali journalism.

Economic Constraints
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the financial struggles of media organizations. A national survey conducted in 2020 revealed that many journalists faced job losses, salary cuts, and increased job insecurity. The economic downturn led to reduced advertising revenues, forcing media houses to downsize and, in some cases, shut down operations.
Digital Transformation and Misinformation
The rapid shift to digital platforms has transformed the media landscape. While this has increased accessibility, it has also led to challenges in maintaining journalistic standards. The proliferation of misinformation and the decline in investigative journalism have raised concerns about media credibility. A 2022 article highlighted the declining standards of journalism, emphasizing the spread of misinformation and its impact on democratic institutions.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Journalists have faced legal challenges, including arrests and lawsuits under various pretexts, which have been used to suppress critical reporting. The misuse of cybercrime laws to target journalists has been a particular concern, with reports indicating ambiguous court decisions and inadequate protection for journalists.
Intersection of Climate Change and Journalism
Reporting on climate change in Nepal’s Himalayan region presents unique challenges. Journalists must navigate complex scientific information, often with limited resources and training. The economic constraints faced by media organizations further limit the capacity for in-depth environmental reporting. Additionally, the risks associated with reporting in remote and disaster-prone areas pose safety concerns for journalists.
The period between 2020 and 2022 has been marked by significant challenges in both the environmental and media landscapes of Nepal. The impacts of climate change in the Himalayan region underscore the need for robust adaptation strategies and sustainable practices. Simultaneously, the difficulties faced by journalism highlight the importance of safeguarding press freedom, ensuring economic viability, and adapting to the digital transformation. Addressing these challenges is crucial for fostering an informed and resilient society capable of navigating the complexities of climate change and upholding democratic values.